Ⅰ. Power Supplies - External/Internal (Off-Board)
Ⅱ. Electrical Characteristics of Power Supplies - External/Internal (Off-Board)
Ⅲ. Physical Characteristics of Power Supplies - External/Internal (Off-Board)
A power supply is an essential component in any electronic device or system, providing a stable and reliable source of electrical energy. Power supplies can be either internal or external (off-board), each with its advantages and disadvantages. Power Supplies - External/Internal (Off-Board)
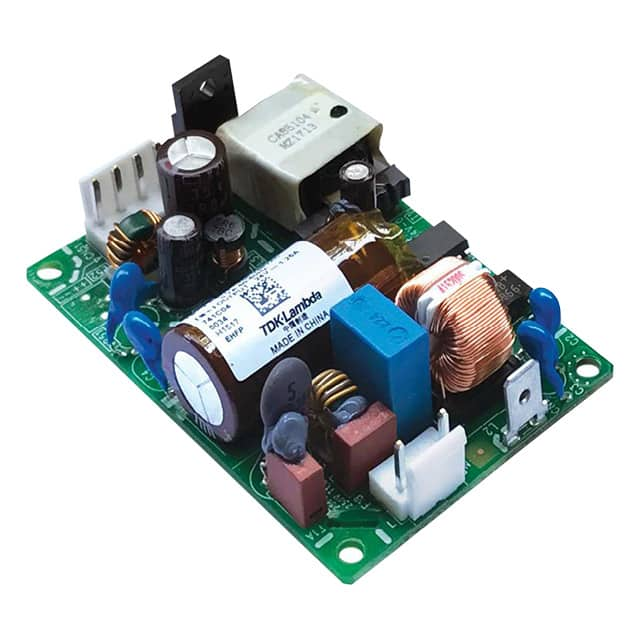

Internal power supplies are built into the device they power, such as desktop computers, servers, and other electronic equipment. They are typically more reliable and efficient than external power supplies, as they are designed to work specifically with the device and have more robust protections against electrical interference. However, replacing or repairing an internal power supply can be challenging, and it may require the device to be disassembled.
External power supplies, on the other hand, are separate devices that plug into the device they power. They are commonly used for laptops, mobile phones, and other portable devices, as well as household appliances like TVs and game consoles. External power supplies are typically less expensive than internal power supplies and can be easily replaced if they fail or become damaged. However, they may be less efficient and reliable than internal power supplies, as they may be more susceptible to electrical interference.
Both internal and external power supplies can be either AC-to-DC or DC-to-DC converters, depending on the device's power requirements. AC-to-DC converters convert the alternating current (AC) from the power outlet into direct current (DC), which is required by most electronic devices. DC-to-DC converters are used to convert one DC voltage level to another, and are commonly used in devices that require multiple voltage levels.
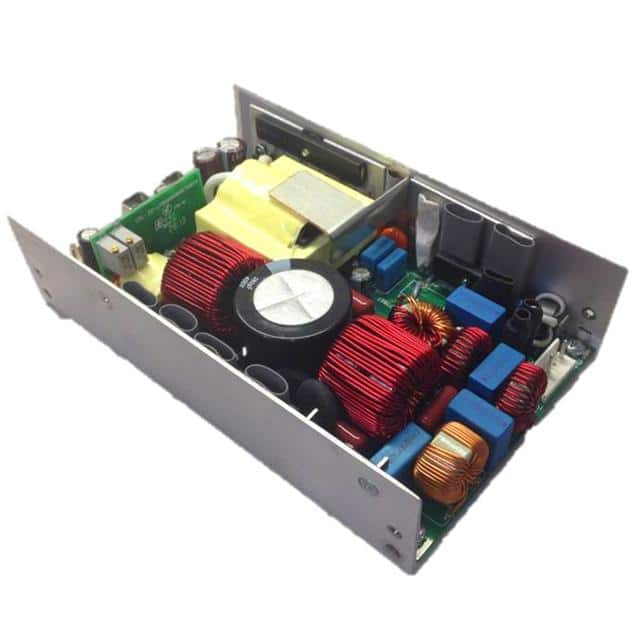

The choice between an internal or external power supply depends on the specific needs of the device and the application. Internal power supplies are generally more reliable and efficient but can be difficult to replace or repair. External power supplies are less expensive and easier to replace but may be less efficient and reliable.
Electrical Characteristics of Power Supplies - External/Internal (Off-Board)
In addition to physical characteristics, power supplies also have electrical characteristics that are important to consider when choosing the right power supply for a device. Here are some of the important electrical characteristics of power supplies:
Input voltage: The input voltage of a power supply refers to the voltage level it requires from the AC power source, typically 110-120V or 220-240V.
Input current: The input current of a power supply refers to the amount of current it draws from the AC power source. This is typically measured in amps (A) and is important to ensure that the power supply is compatible with the electrical circuit it is connected to.
Output voltage: The output voltage of a power supply refers to the voltage level it provides to the device it is powering. Different devices require different voltage levels, so it's important to choose a power supply with the appropriate output voltage.
Output current: The output current of a power supply refers to the amount of current it can supply to the device it is powering. This is typically measured in amps (A) and is important to ensure that the power supply can meet the device's power requirements.
Ripple and noise: Ripple and noise are electrical disturbances that can affect the performance of a device. Power supplies have specifications for the maximum amount of ripple and noise they can produce, which is important to consider when choosing a power supply for a sensitive device.
Efficiency: The efficiency of a power supply refers to the percentage of energy it converts from the AC power source to the DC power delivered to the device. Higher efficiency power supplies waste less energy and generate less heat.
Power factor correction (PFC): Power factor correction is a technology used in some power supplies to improve their efficiency and reduce harmonic distortion in the AC power source.
Understanding these electrical characteristics of power supplies can help in selecting the right power supply for a device, ensuring it has the appropriate voltage and current output, as well as other important features like efficiency and PFC.
Physical Characteristics of Power Supplies - External/Internal (Off-Board)
Power supplies, whether internal or external, have some common physical characteristics that determine their compatibility and functionality. Here are some of the important physical characteristics of power supplies:
Form factor: The form factor of a power supply refers to its physical shape and dimensions. Different devices may require power supplies with different form factors, such as ATX, SFX, TFX, and others.
Wattage: The wattage of a power supply refers to the maximum amount of power it can provide to the device it is powering. Higher wattage power supplies are generally required for more demanding applications or devices.
Voltage: The voltage of a power supply refers to the electrical potential difference between its positive and negative terminals. Different devices require different voltages, such as 12V, 24V, or 48V.
Current: The current of a power supply refers to the flow of electrical charge through it. Different devices require different amounts of current, which is measured in amperes (A).
Connectors: Power supplies have different types and numbers of connectors that allow them to connect to various devices. For example, ATX power supplies have a 20+4 pin main connector, SATA power connectors for hard drives, and Molex connectors for other peripherals.
Efficiency: The efficiency of a power supply refers to the percentage of energy it converts from the AC power source to the DC power delivered to the device. Higher efficiency power supplies waste less energy and generate less heat.
Cooling: Power supplies generate heat during operation, and most require cooling to prevent overheating. Some power supplies use fans, while others use passive cooling methods such as heat sinks.
The physical characteristics of a power supply play a critical role in its compatibility and functionality with different devices. Understanding these characteristics can help in choosing the right power supply for a specific application or device.
标签:power supply